Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the Python issuperset() method to check if a set is a superset of another.
Introduction to Python issuperset method
Suppose that you have two sets: A and B. Set A is a superset of set B if all elements of set B are elements of set A.
If set A is a superset of set B, then set B is a subset of set A. To check if a set is a subset of another, you use the issubset() method.
If set A and set B are not equal, set A is a proper superset of set B.
Logically, a set is a superset of itself.
The following illustrates that set A is the superset of the set B because the elements 1, 2, 3 in the set B are also in set A:
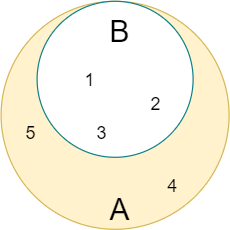
In Python, you use the set issuperset() method to check if a set is a superset of another set:
set_a.issuperset(set_b)Code language: Python (python)The issuperset() returns True if the set_a is a superset of the set_b. Otherwise, it returns False.
Python issuperset() method examples
The following example uses the issuperset() to check if the numbers set is a superset of the scores set:
numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} scores = {1, 2, 3} result = numbers.issuperset(scores) print(result)Code language: Python (python)Output:
TrueCode language: Python (python)Since all elements of the scores set are present in the numbers set, the numbers set is the superset of the scores set.
A set is also a superset of itself. For example:
numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} result = numbers.issuperset(numbers) print(result)Code language: Python (python)Output:
TrueCode language: Python (python)The scores set is not a subset of the numbers set therefore the following example returns False:
numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} scores = {1, 2, 3} result = scores.issuperset(numbers) print(result)Code language: Python (python)Output:
FalseCode language: Python (python)Using superset operators
The >= operator determines if a set is a superset of another set:
set_a >= set_bCode language: Python (python)The >= operator returns True if the set_a is a superset of the set_b. Otherwise, it returns False. For example:
numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} scores = {1, 2, 3} result = numbers >= scores print(result) # True result = numbers >= numbers print(result) # TrueCode language: Python (python)Output:
True TrueCode language: Python (python)To check if a set is a proper superset of another set, you use the > operator:
set_a > set_bCode language: Python (python)For example:
numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} scores = {1, 2, 3} result = numbers > scores print(result) # True result = numbers > numbers print(result) # TrueCode language: Python (python)Output:
True FalseCode language: Python (python)In this example, the set numbers is not a proper superset of itself, therefore, the > operator returns False.
Leave a Reply