Django provides a Form class which is used to create HTML forms. It describes a form and how it works and appears.
It is similar to the ModelForm class that creates a form by using the Model, but it does not require the Model.
Each field of the form class map to the HTML form <input> element and each one is a class itself, it manages form data and performs validation while submitting the form.
Lets see an example, in which we are creating some fields too.
from django import forms
class StudentForm(forms.Form):
firstname = forms.CharField(label="Enter first name",max_length=50)
lastname = forms.CharField(label="Enter last name", max_length = 100) A StudentForm is created that contains two fields of CharField type. Charfield is a class and used to create an HTML text input component in the form.
The label is used to set HTML label of the component and max_length sets length of an input value.
When rendered, it produces the following HTML to the browser.
<label for="id_firstname">Enter first name:</label>
<input type="text" name="firstname" required maxlength="50" id="id_firstname" />
<label for="id_lastname">Enter last name:</label> <input type="text" name="lastname" required maxlength="100" id="id_lastname" /> Note: Django Form does not include <form> tags, or a submit button. We’ll have to provide those ourselves in the template.
Commonly used fields and their details are given in the below table.
| Name | Class | HTML Input | Empty value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BooleanField | class BooleanField(**kwargs) | CheckboxInput | False |
| CharField | class CharField(**kwargs) | TextInput | Whatever you’ve given as empty_value. |
| ChoiceField | class ChoiceField(**kwargs) | Select | ” (an empty string) |
| DateField | class DateField(**kwargs) | DateInput | None |
| DateTimeField | class DateTimeField(**kwargs) | DateTimeInput | None |
| DecimalField | class DecimalField(**kwargs) | NumberInput | None |
| EmailField | class EmailField(**kwargs) | EmailInput | ” (an empty string) |
| FileField | class FileField(**kwargs) | ClearableFileInput | None |
| ImageField | class ImageField(**kwargs) | ClearableFileInput | None |
Let’s see a complete example to create an HTML form with the help of Django Form class.
Building a Form in Django
Suppose we want to create a form to get Student information, use the following code.
from django import forms
class StudentForm(forms.Form):
firstname = forms.CharField(label="Enter first name",max_length=50)
lastname = forms.CharField(label="Enter last name", max_length = 100) Put this code into the forms.py file.
Instantiating Form in Django
Now, we need to instantiate the form in views.py file. See, the below code.
// views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from myapp.form import StudentForm
def index(request):
student = StudentForm()
return render(request,"index.html",{'form':student}) Passing the context of form into index template that looks like this:
// index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Index</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="POST" class="post-form">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button type="submit" class="save btn btn-default">Save</button>
</form>
</body>
</html> Provide the URL in urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from myapp import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('index/', views.index), - ]
Run Server and access the form at browser by localhost:8000/index, and it will produce the following output.
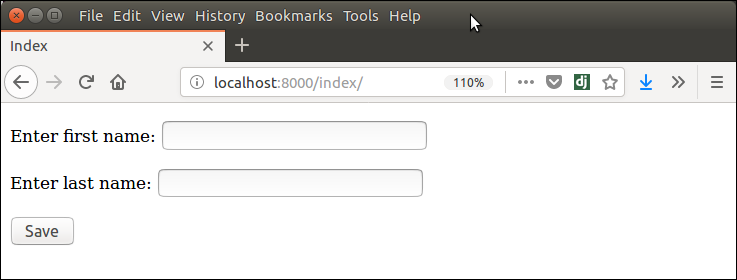
There are other output options though for the <label>/<input> pairs:
- {{ form.as_table }} will render them as table cells wrapped in <tr> tags
- {{ form.as_p }} will render them wrapped in <p> tags
- {{ form.as_ul }} will render them wrapped in <li> tags
Leave a Reply