An exception is an abnormal event that leads to program failure. To deal with this situation, Django uses its own exception classes and supports all core Python exceptions as well.
Django core exceptions classes are defined in django.core.exceptions module. This module contains the following classes.
Django Exception Classes
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| AppRegistryNotReady | It is raised when attempting to use models before the app loading process. |
| ObjectDoesNotExist | The base class for DoesNotExist exceptions. |
| EmptyResultSet | If a query does not return any result, this exception is raised. |
| FieldDoesNotExist | It raises when the requested field does not exist. |
| MultipleObjectsReturned | This exception is raised by a query if only one object is expected, but multiple objects are returned. |
| SuspiciousOperation | This exception is raised when a user has performed an operation that should be considered suspicious from a security perspective. |
| PermissionDenied | It is raised when a user does not have permission to perform the action requested. |
| ViewDoesNotExist | It is raised by django.urls when a requested view does not exist. |
| MiddlewareNotUsed | It is raised when a middleware is not used in the server configuration. |
| ImproperlyConfigured | The ImproperlyConfigured exception is raised when Django is somehow improperly configured. |
| FieldError | It is raised when there is a problem with a model field. |
| ValidationError | It is raised when data validation fails form or model field validation. |
Django URL Resolver Exceptions
These exceptions are defined in django.urls module.
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| Resolver404 | This exception raised when the path passed to resolve() function does not map to a view. |
| NoReverseMatch | It is raised when a matching URL in your URLconf cannot be identified based on the parameters supplied. |
Django Database Exceptions
The following exceptions are defined in django.db module.
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| DatabaseError | It occurs when the database is not available. |
| IntegrityError | It occurs when an insertion query executes. |
| DataError | It raises when data related issues come into the database. |
Django Http Exceptions
The following exceptions are defined in django.http module.
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| UnreadablePostError | It is raised when a user cancels an upload. |
Django Transaction Exceptions
The transaction exceptions are defined in django.db.transaction.
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| TransactionManagementError | It is raised for any and all problems related to database transactions. |
Django Exception Example
Suppose, we want to get employee record where id = 12, our view function will look below. It raises a DoesNotExist exception if data not found. This is Django’s built-in exception.
// views.py
def getdata(request):
data = Employee.objects.get(id=12)
return HttpResponse(data)// urls.py
path('get',views.getdata) It shows the following exception because no record is available at id 12.
Output:
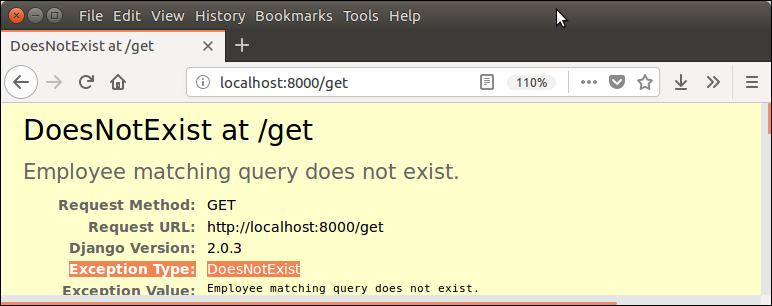
We can handle it by using try and except, now let’s handle this exception.
// Views.py
def getdata(request):
try:
data = Employee.objects.get(id=12)
except ObjectDoesNotExist:
return HttpResponse("Exception: Data not found")
return HttpResponse(data);Output:
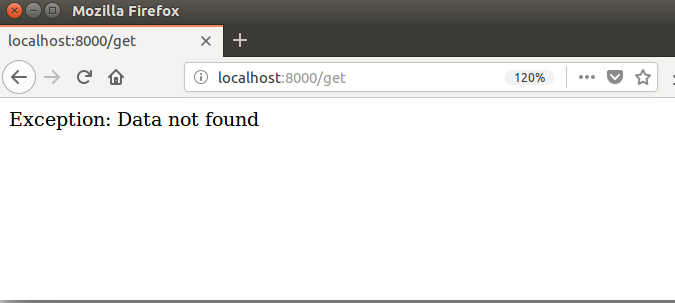
Leave a Reply