Flask class provides the redirect() function which redirects the user to some specified URL with the specified status code.
An HTTP status code is a response from the server to the request of the browser. When we visit a website, a request is sent to the server, and the server then responds to the browser’s request with a three-digit code: the HTTP status code. This status code also represents the error.
The syntax to use the redirect() function is given below.
Flask.redirect(<location>,<status-code>, <response> ) It accepts the following parameters.
| SN | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | location | It is the URL where the response will be redirected. |
| 2 | status code | It is the status code that is sent to the browser’s header along with the response from the server. |
| 3 | response | It is the instance of the response that is used in the project for future requirements. |
Consider the following example where the user is redirected to the success page with the HTTP status code 302 (found) on the successful login otherwise; the user reverts to this page only.
Example
login.py
from flask import *
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def home ():
return render_template("home.html")
@app.route('/login')
def login():
return render_template("login.html");
@app.route('/validate', methods = ["POST"])
def validate():
if request.method == 'POST' and request.form['pass'] == 'jtp':
return redirect(url_for("success"))
return redirect(url_for("login"))
@app.route('/success')
def success():
return "logged in successfully"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug = True)home.html
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>home</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <h3>Welcome to the website</h3>
- <a href = "/login">login</a><br>
- </html>
login.html
<html>
<head>
<title>login</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method = "post" action = "http://localhost:5000/validate">
<table>
<tr><td>Email</td><td><input type = 'email' name = 'email'></td></tr>
<tr><td>Password</td><td><input type = 'password' name = 'pass'></td></tr>
<tr><td><input type = "submit" value = "Submit"></td></tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>In the above example, the URL ‘/’ contains a link to the login page as shown in the below image.
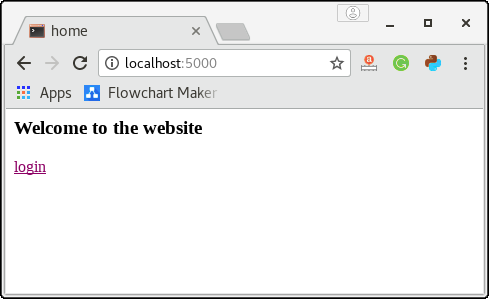
The login page contains shown in the below image prompts the user to enter the email and password, and the submit button redirects the user to URL /validate.
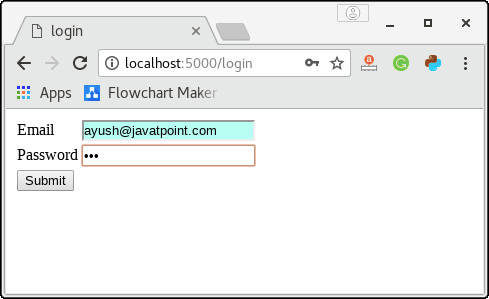
In this case, as I have entered a random password not equal to ‘jtp’ therefore, the user reverts to this page (login page) only.
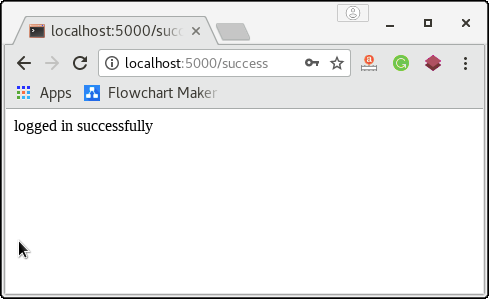
However, the user is redirected to the URL /success only if the password entered by the user to ‘jtp‘. The URL http://localhost:5000/success (generated on the successful login) is shown in the below image.
Standard HTTP Codes
The following HTTP codes are standardized.
HTTP_300_MULTIPLE_CHOICES
HTTP_301_MOVED_PERMANENTLY
HTTP_302_FOUND
HTTP_303_SEE_OTHER
HTTP_304_NOT_MODIFIED
HTTP_305_USE_PROXY
HTTP_306_RESERVED
HTTP_307_TEMPORARY_REDIRECTThe default status code is HTTP_302_FOUND.
The abort() function
The abort() function is used to handle the cases where the errors are involved in the requests from the client side, such as bad requests, unauthorized access and many more. However, the error code is to be mentioned due to which the error occurred.
The syntax to use the abort() function is given below.
- Flask.abort(code)
We can mention the following error codes depending upon the specified errors.
- 400: for bad requests
- 401: for unauthorized access
- 403: for forbidden
- 404: for not found
- 406: for not acceptable
- 415: for unsupported media types
- 429: for too many requests
Let’s modify the script login.py from the above example and use the abort() function with the error code 401 (for unauthorized access) in the case of any random password entered by the user.
Example
from flask import *
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def home ():
return render_template("home.html")
@app.route('/login')
def login():
return render_template("login.html");
@app.route('/validate', methods = ["POST"])
def validate():
if request.method == 'POST' and request.form['pass'] == 'jtp':
return redirect(url_for("success"))
else:
abort(401)
@app.route('/success')
def success():
return "logged in successfully"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug = True)It will generate the following result in the case of the wrong password.
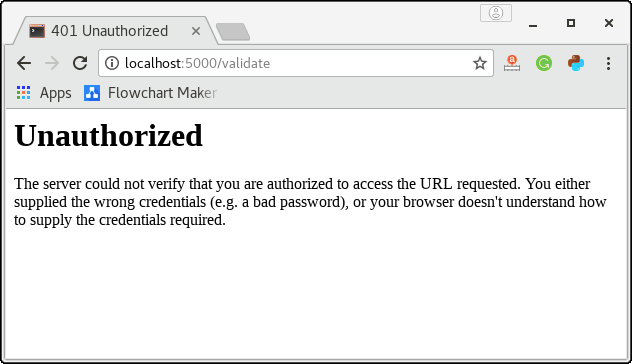
Here, we have used the error code 401 since the user has requested the unauthorized access to the resource. We can change it to any code depending upon the error case.
Leave a Reply