Relations can be represented in many ways. Some of which are as follows:
1. Relation as a Matrix: Let P = [a1,a2,a3,…….am] and Q = [b1,b2,b3……bn] are finite sets, containing m and n number of elements respectively. R is a relation from P to Q. The relation R can be represented by m x n matrix M = [Mij], defined as
Mij = 0 if (ai,bj) ∉ R
1 if (ai,bj )∈ R
Example
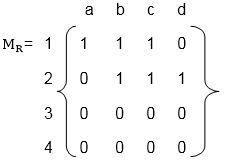
- Let P = {1, 2, 3, 4}, Q = {a, b, c, d}
- and R = {(1, a), (1, b), (1, c), (2, b), (2, c), (2, d)}.
The matrix of relation R is shown as fig:
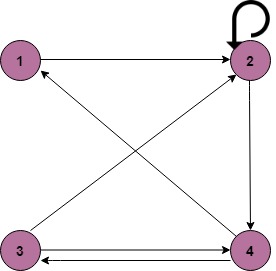
2. Relation as a Directed Graph: There is another way of picturing a relation R when R is a relation from a finite set to itself.
Example
- A = {1, 2, 3, 4}
- R = {(1, 2) (2, 2) (2, 4) (3, 2) (3, 4) (4, 1) (4, 3)}
3. Relation as an Arrow Diagram: If P and Q are finite sets and R is a relation from P to Q. Relation R can be represented as an arrow diagram as follows.
Draw two ellipses for the sets P and Q. Write down the elements of P and elements of Q column-wise in three ellipses. Then draw an arrow from the first ellipse to the second ellipse if a is related to b and a ∈ P and b ∈ Q.
Example
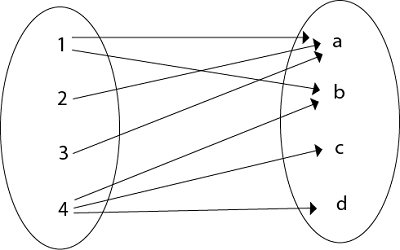
- Let P = {1, 2, 3, 4}
- Q = {a, b, c, d}
- R = {(1, a), (2, a), (3, a), (1, b), (4, b), (4, c), (4, d)
The arrow diagram of relation R is shown in fig:
4. Relation as a Table: If P and Q are finite sets and R is a relation from P to Q. Relation R can be represented in tabular form.
Make the table which contains rows equivalent to an element of P and columns equivalent to the element of Q. Then place a cross (X) in the boxes which represent relations of elements on set P to set Q.
Example
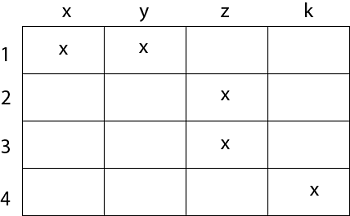
- Let P = {1, 2, 3, 4}
- Q = {x, y, z, k}
- R = {(1, x), (1, y), (2, z), (3, z), (4, k)}.
The tabular form of relation as shown in fig:
Leave a Reply