Congruent triangles have the same size and the same shape. When triangles are congruent, all corresponding sides and corresponding angles are also congruent or equal. For example, the two triangles below are congruent.
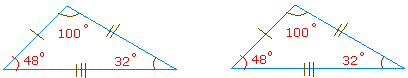
Corresponding angles are angles in the same position.
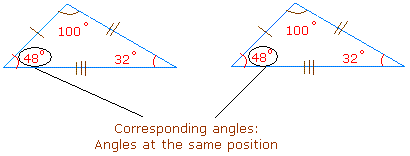
Corresponding sides are sides that are in the same position.
The two triangles above have a side with 3 markings. These sides are in the same position and thus are corresponding.
Congruent sides are sides that have equal measures.
Congruent angles are angles that have equal corresponding sides and equal measures.
In the triangle above, if we pull out the side with one and three markings and the included angle, we get the following:
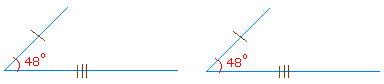
The above 48 degrees angle is a good example of congruent angles because the sides are equal and the angles are equal.
Included side: A side between two angles
Included angle: An angle between two sides
Using postulates and theorem to check if two triangles are congruent triangles.
There are three postulates and two theorems that are used to identify if two triangles are congruent.
With these postulates and theorems, you don’t have to check if all corresponding angles and all sides are congruent.
If the triangles meet the condition of the postulate or theorem, then you have congruent triangles.
They are the SSS postulate, SAS postulate, ASA postulate, AAS theorem, and Hypotenuse-Leg theorem.
SSS postulate:
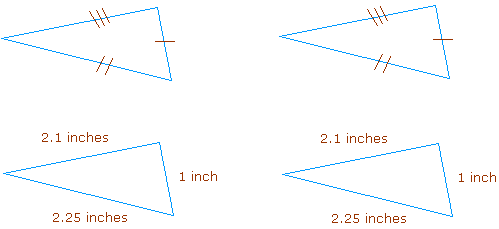
If three sides of a triangle are congruent to three sides of a second triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
Example:
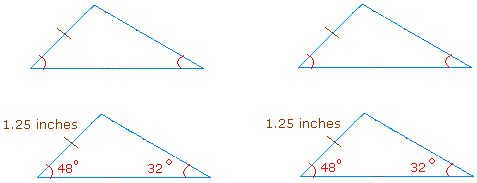
ASA postulate:
If two angles and the side between these two angles (included side) of one triangle are congruent to the corresponding angles and the included side of a second triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
Example:
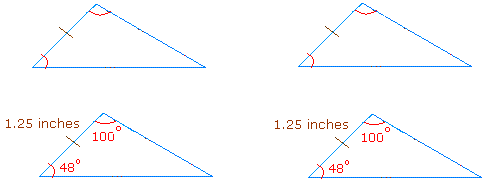
SAS postulate:
If two sides and the angle between these two sides (included angle) of one triangle are congruent to the corresponding two sides and the included angle of a second triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
Example:
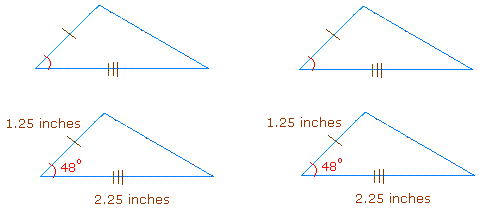
AAS theorem:
If two angles and a side not between these two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles and the corresponding side not between these two angles of a second triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
Example:
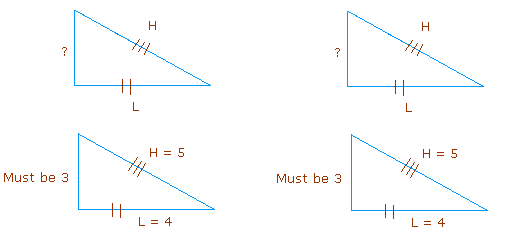
Hypotenuse-Leg theorem:
If the hypotenuse and leg of a right triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and corresponding leg of a second right triangle, then the two triangles are congruent
Example:
Leave a Reply