The MathML <mo> element is used to specify an operator on a web page. It can specify any type of operator for example: =, +, ?, ?, and even parentheses and commas.
Let’s take an expression to deploy an operator.
3 x – 2 y
Equivalent code:
- <math xmlns=’http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML’ display=’block’ >
- <mn>3</mn>
- <mi>x</mi>
- <mo>–</mo>
- <mn>2</mn>
- <mi>y</mi>
- </math>
Note: Traditional typography differentiates hyphens from minus signs, which are longer. In the above HTML code, we used a hyphen, but since we put it in an element, the browser read it as a minus sign.
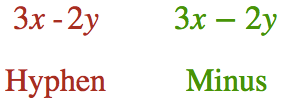
Operator Entities
Operator entities are used to represent special symbols like minus signs, less than, greater than etc. HTML offers several character entities dedicated to mathematics. A list of most common operators:
| Index | Symbol | Entity | Hex | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1) | ? | − | − | Subtraction |
| 2) | * | × | × | Multiplication |
| 3) | / | ÷ | ÷ | Division |
| 4) | ≠ | ≠ | ≠ | Not equal |
| 5) | ≈ | ≈ | ≈ | Approximately equal |
| 6) | < | < | < | Less than |
| 7) | ≤ | ≤ | ≤ | Less than or equal |
| 8) | > | > | > | Greater than |
| 9) | ≥ | ≥ | ≥ | Greater than or equal |
| 10) | ± | ± | ± | Plus or minus |
The operator entities are generally used as the content of an element:
Example:
Let’s take an example to see the use of operators in MathML.
See this equation: 5 x – 4 y ? 0
Equivalent code:
- <math xmlns=’http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML’ display=’block’>
- <mn>5</mn>
- <mi>x</mi>
- <mo>–</mo>
- <mn>4</mn>
- <mi>y</mi>
- <mo>≥</mo>
- <mn>0</mn>
- </math>
Supporting Browsers:
| Element |  Chrome Chrome |  IE IE |  Firefox (Gecko) Firefox (Gecko) |  Opera Opera |  Safari Safari |
| <mo> | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Only Basic Support |
Leave a Reply