SQLite commands are similar to SQL commands. There are three types of SQLite commands:
- DDL: Data Definition Language
- DML: Data Manipulation Language
- DQL: Data Query Language
Data Definition Language
There are three commands in this group:
CREATE: This command is used to create a table, a view of a table or other object in the database.
ALTER: It is used to modify an existing database object like a table.
DROP: The DROP command is used to delete an entire table, a view of a table or other object in the database.
Data Manipulation language
There are three commands in data manipulation language group:
INSERT: This command is used to create a record.
UPDATE: It is used to modify the records.
DELETE: It is used to delete records.
Data Query Language
SELECT: This command is used to retrieve certain records from one or more table.
SQLite dot Command
Following is a list of SQLite dot commands. These commands are not terminated by a semicolon (;).
.help command:
Check the list of dot commands by using the “.help” at anytime.
For example:
Sqlite> .help 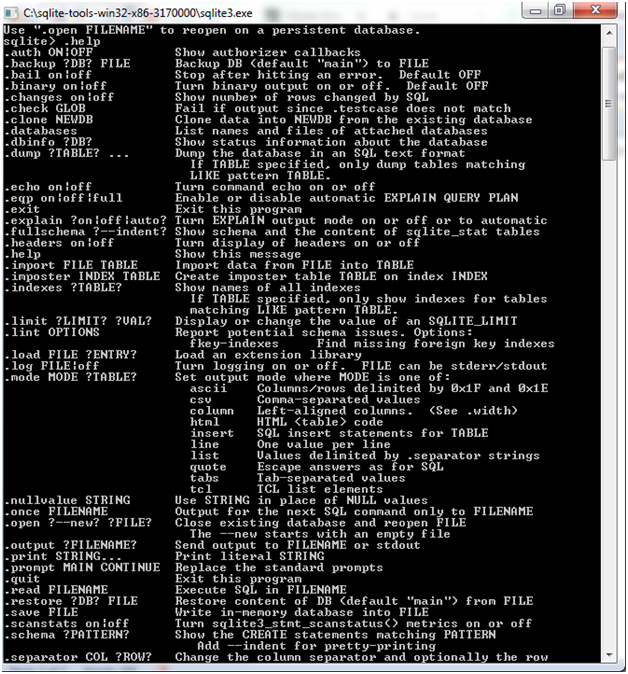
The above are the list of various important SQLite dot commands. See these commands with description in the following table:
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
| .backup ?db? file | backup DB (default “main”) to file |
| .bail on|off | stop after hitting an error. default off |
| .databases | list names and files of attached databases |
| .dump ?table? | dump the database in an sql text format. if table specified, only dump tables matching like pattern table. |
| .echo on|off | turn command echo on or off |
| .exit | exit sqlite prompt |
| .explain on|off | turn output mode suitable for explain on or off. with no args, it turns explain on. |
| .header(s) on|off | turn display of headers on or off |
| .help | show this message |
| .import file table | import data from file into table |
| .indices ?table? | show names of all indices. if table specified, only show indices for tables matching like pattern table. |
| .load file ?entry? | load an extension library |
| .log file|off | turn logging on or off. file can be stderr/stdout |
| .mode mode | set output mode where mode is one of:<br/><div>csv:comma-separated values <br/><br> <div><div>column: left-aligned columns.<br/><div>html: html <table> code<br/> <div>insert: sql insert statements for table<br/><div>line: one value per line<br/> <div>list: values delimited by .separator string<br/><div>tabs: tab-separated values<br/> <div>tcl: tcl list elements<br/> |
| .nullvalue string | print string in place of null values |
| .output filename | send output to filename |
| .output stdout | send output to the screen |
| .print string… | print literal string |
| .prompt main continue | replace the standard prompts |
| .quit | exit sqlite prompt |
| .read filename | execute sql in filename |
| .schema ?table? | show the create statements. if table specified, only show tables matching like pattern table. |
| .separator string | change separator used by output mode and .import |
| .show | show the current values for various settings |
| .stats on|off | turn stats on or off |
| .tables ?pattern? | list names of tables matching a like pattern |
| .timeout ms | try opening locked tables for ms milliseconds |
| .width num num | set column widths for “column” mode |
| .timer on|off | turn the cpu timer measurement on or off |
.show command:
You can use the .show command to see default setting of for your SQLite command prompt.
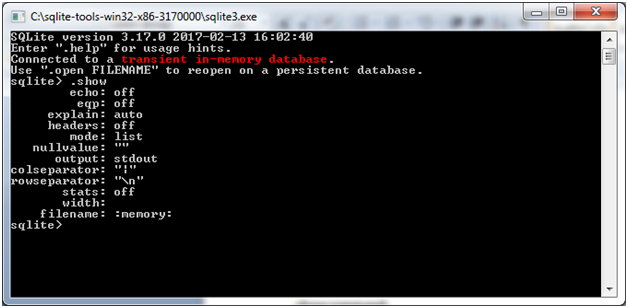
Note: Don’t put space between sqlite> prompt and dot command, otherwise it will not work.
Special dot commands
There are some dot commands which are used to format your output. These commands are:
.header on
.mode column
.timer on
Leave a Reply