Word problems with division often involve sharing from a total number. Take note which number is the dividend and which should be the divisor to solve the problem correctly.
Example:
Rosie has 60 sweets. If she gave her friends 3 sweets each, how many friends can she share her sweets with?
Solution:
[60 sweets] ÷ [3 for each friend]
60 ÷ 3 = 20 friends
Dividing can also be seen as a number of times that one quantity can be taken from a total. Take note what the question is asking for – sometimes the question may ask for the remainder rather than the quotient.
Example:
Sam has $17. He wants to buy some hot dogs at $3 each.
a) How many hot dogs can he buy?
b) How much money would he have left?
Solution:
[$17] ÷ [3 per hot dog]
17 ÷ 3 = 5 R 2
a) He can buy 5 hot dogs (Answer from the quotient)
b) He would have $2 left (Answer from the remainder)
Math: Numbers
These lessons look at the relationship between the different types of numbers.
We all work with numbers every day, often without really thinking about them: numbers on the newspaper (prices, dates,amounts); numbers on the television or radio; sporting results; time; labels on food; money; addresses, bar codes and many more.
The following diagram shows the relationship between the types of numbers. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on types of numbers.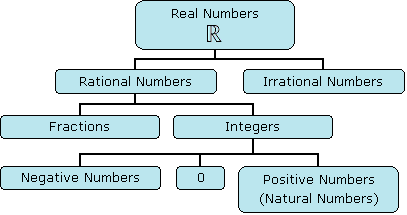
Natural numbers
Natural numbers are positive integers. E.g. 1, 2, 3, …
Whole numbers
Some authors take whole numbers to be 0, 1, 2, 3, …
Other authors may consider whole numbers as
… –4, –3, –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, …
which makes whole numbers the same as integers.
Rational numbers
Rational numbers are numbers that can be written as a fraction where the numerator and denominator are integers.![]()
Irrational numbers
Irrational numbers are numbers that are not rational. In other words, they are numbers that cannot be written as fractions.
In decimal form, these numbers go on forever and the same pattern of digits are not repeated.
For example: pi(π) = 3.142.. and √2 = 1.4142…
Real numbers
Real numbers are all the rational and irrational numbers.
Classifying Real Numbers
This video explains the different classifications of Real Numbers and has a number of examples.
The following video will describe what are natural numbers, integers, rational numbers and more.
Squares
The square of a number is the number multiplied by itself.
For example: square of 4 = 4 2 = (4 × 4) = 16
Perfect squares are squares of whole numbers.
Some examples of perfect squares are
12 = 1, 22 = 4, 32 = 9, 42 = 16, 52 = 25, 62 = 36
Square roots
The square root of a number n is the number that gives n when multiplied by itself.
For example: square root of 49 = 7 because (7 × 7) = 49
The square root of a perfect square would be a whole number.![]()
Cubes
The cube of a number is the number multiplied by itself twice
For example: cube of 4 = 4 3 = (4 × 4 × 4) = 64
Perfect cubes are cubes of whole numbers.
Some examples of cubes are 13 = 1, 23 = 8, 33 = 27, 43 = 64, 53 = 125, 63 = 216
Cube roots
The cube root of a number n is the number that gives n when multiplied by itself twice.
For example: cube root of 27 = 3 because (3 × 3 × 3) = 27
The cube root of a perfect cube would be a whole number.![]()
Leave a Reply