In the previous topic, we have installed Django successfully. Now, we will learn step by step process to create a Django application.
To create a Django project, we can use the following command. projectname is the name of Django application.
$ django-admin startproject projectname Django Project Example
Here, we are creating a project djangpapp in the current directory.
- $ django-admin startproject djangpapp
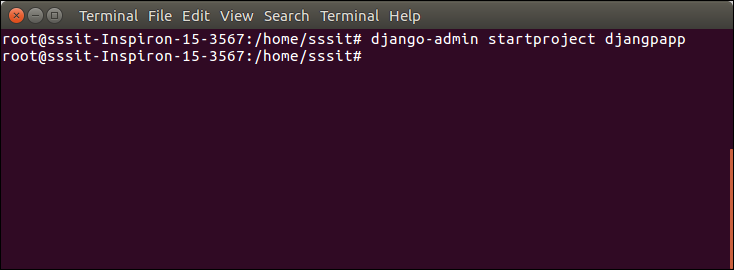
Locate into the Project
Now, move to the project by changing the directory. The Directory can be changed by using the following command.
- cd djangpapp
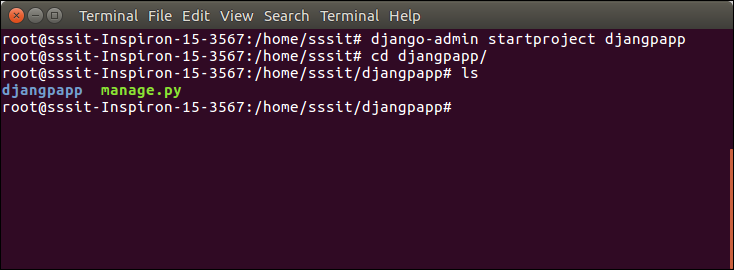
To see all the files and subfolders of django project, we can use tree command to view the tree structure of the application. This is a utility command, if it is not present, can be downloaded via apt-get install tree command.
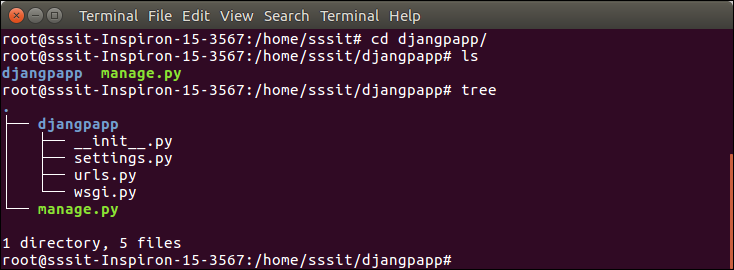
A Django project contains the following packages and files. The outer directory is just a container for the application. We can rename it further.
- manage.py: It is a command-line utility which allows us to interact with the project in various ways and also used to manage an application that we will see later on in this tutorial.
- A directory (djangpapp) located inside, is the actual application package name. Its name is the Python package name which we’ll need to use to import module inside the application.
- __init__.py: It is an empty file that tells to the Python that this directory should be considered as a Python package.
- settings.py: This file is used to configure application settings such as database connection, static files linking etc.
- urls.py: This file contains the listed URLs of the application. In this file, we can mention the URLs and corresponding actions to perform the task and display the view.
- wsgi.py: It is an entry-point for WSGI-compatible web servers to serve Django project.
Initially, this project is a default draft which contains all the required files and folders.
Running the Django Project
Django project has a built-in development server which is used to run application instantly without any external web server. It means we don’t need of Apache or another web server to run the application in development mode.
To run the application, we can use the following command.
- $ python3 manage.py runserver
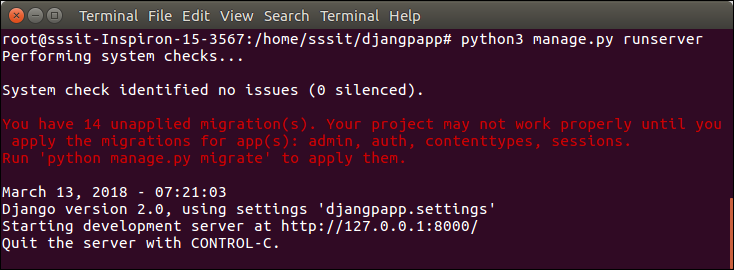
Look server has started and can be accessed at localhost with port 8000. Let’s access it using the browser, it looks like the below.
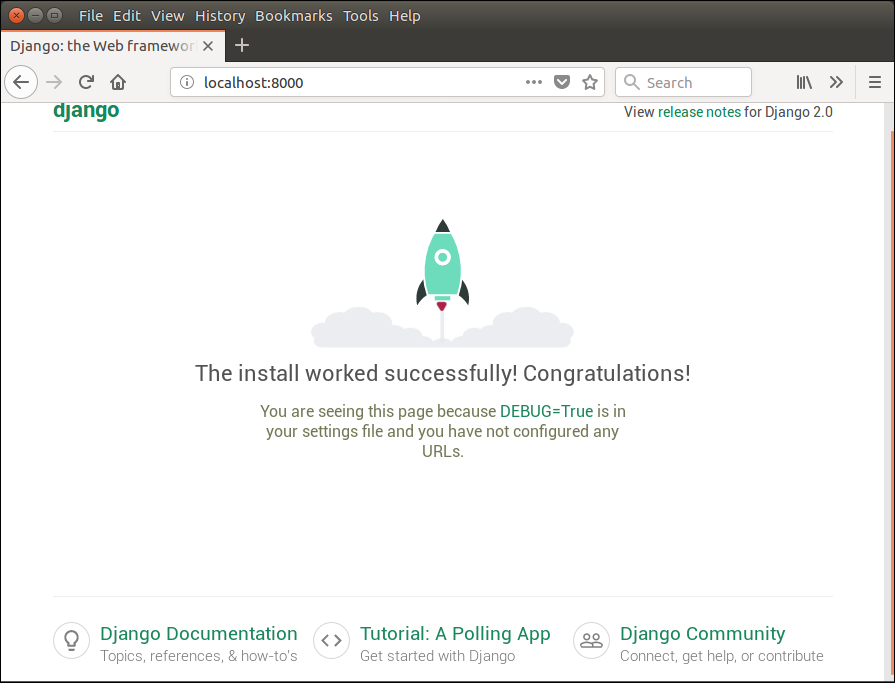
The application is running successfully. Now, we can customize it according to our requirement and can develop a customized web application.
Leave a Reply