In Django, a model is a class which is used to contain essential fields and methods. Each model class maps to a single table in the database.
Django Model is a subclass of django.db.models.Model and each field of the model class represents a database field (column).
Django provides us a database-abstraction API which allows us to create, retrieve, update and delete a record from the mapped table.
Model is defined in Models.py file. This file can contain multiple models.
Let’s see an example here, we are creating a model Employee which has two fields first_name and last_name.
from django.db import models
class Employee(models.Model):
first_name = models.CharField(max_length=30)
last_name = models.CharField(max_length=30) The first_name and last_name fields are specified as class attributes and each attribute maps to a database column.
This model will create a table into the database that looks like below.
CREATE TABLE appname_employee (
"id" INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
"first_name" varchar(30) NOT NULL,
"last_name" varchar(30) NOT NULL
); The created table contains an auto-created id field. The name of the table is a combination of app name and model name that can be changed further.
Register / Use Model
After creating a model, register model into the INSTALLED_APPS inside settings.py.
For example,
INSTALLED_APPS = [
#...
'appname',
#...
] Django Model Fields
The fields defined inside the Model class are the columns name of the mapped table. The fields name should not be python reserve words like clean, save or delete etc.
Django provides various built-in fields types.
| Field Name | Class | Particular |
|---|---|---|
| AutoField | class AutoField(**options) | It An IntegerField that automatically increments. |
| BigAutoField | class BigAutoField(**options) | It is a 64-bit integer, much like an AutoField except that it is guaranteed to fit numbers from 1 to 9223372036854775807. |
| BigIntegerField | class BigIntegerField(**options) | It is a 64-bit integer, much like an IntegerField except that it is guaranteed to fit numbers from -9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807. |
| BinaryField | class BinaryField(**options) | A field to store raw binary data. |
| BooleanField | class BooleanField(**options) | A true/false field. The default form widget for this field is a CheckboxInput. |
| CharField | class DateField(auto_now=False, auto_now_add=False, **options) | It is a date, represented in Python by a datetime.date instance. |
| DateTimeField | class DateTimeField(auto_now=False, auto_now_add=False, **options) | It is a date, represented in Python by a datetime.date instance. |
| DateTimeField | class DateTimeField(auto_now=False, auto_now_add=False, **options) | It is used for date and time, represented in Python by a datetime.datetime instance. |
| DecimalField | class DecimalField(max_digits=None, decimal_places=None, **options) | It is a fixed-precision decimal number, represented in Python by a Decimal instance. |
| DurationField | class DurationField(**options) | A field for storing periods of time. |
| EmailField | class EmailField(max_length=254, **options) | It is a CharField that checks that the value is a valid email address. |
| FileField | class FileField(upload_to=None, max_length=100, **options) | It is a file-upload field. |
| FloatField | class FloatField(**options) | It is a floating-point number represented in Python by a float instance. |
| ImageField | class ImageField(upload_to=None, height_field=None, width_field=None, max_length=100, **options) | It inherits all attributes and methods from FileField, but also validates that the uploaded object is a valid image. |
| IntegerField | class IntegerField(**options) | It is an integer field. Values from -2147483648 to 2147483647 are safe in all databases supported by Django. |
| NullBooleanField | class NullBooleanField(**options) | Like a BooleanField, but allows NULL as one of the options. |
| PositiveIntegerField | class PositiveIntegerField(**options) | Like an IntegerField, but must be either positive or zero (0). Values from 0 to 2147483647 are safe in all databases supported by Django. |
| SmallIntegerField | class SmallIntegerField(**options) | It is like an IntegerField, but only allows values under a certain (database-dependent) point. |
| TextField | class TextField(**options) | A large text field. The default form widget for this field is a Textarea. |
| TimeField | class TimeField(auto_now=False, auto_now_add=False, **options) | A time, represented in Python by a datetime.time instance. |
Django Model Fields Example
first_name = models.CharField(max_length=50) # for creating varchar column
release_date = models.DateField() # for creating date column
num_stars = models.IntegerField() # for creating integer column Field Options
Each field requires some arguments that are used to set column attributes. For example, CharField requires mac_length to specify varchar database.
Common arguments available to all field types. All are optional.
| Field Options | Particulars |
|---|---|
| Null | Django will store empty values as NULL in the database. |
| Blank | It is used to allowed field to be blank. |
| Choices | An iterable (e.g., a list or tuple) of 2-tuples to use as choices for this field. |
| Default | The default value for the field. This can be a value or a callable object. |
| help_text | Extra “help” text to be displayed with the form widget. It’s useful for documentation even if your field isn’t used on a form. |
| primary_key | This field is the primary key for the model. |
| Unique | This field must be unique throughout the table. |
Django Model Example
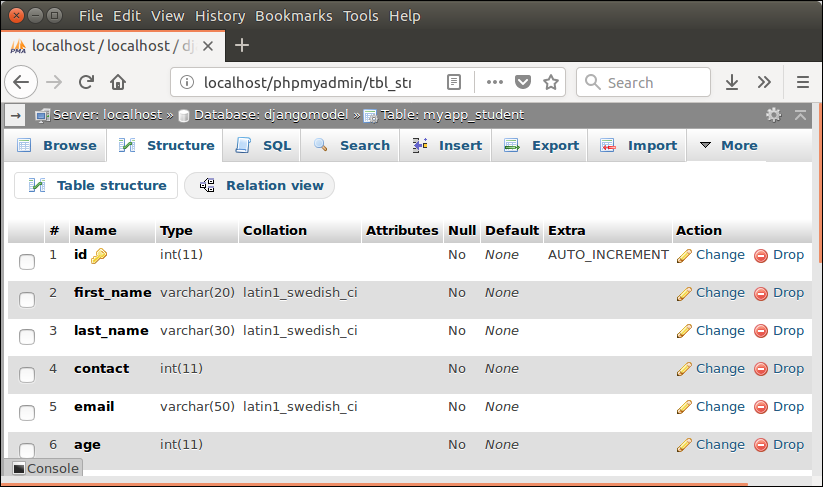
We created a model Student that contains the following code in models.py file.
//models.py
class Student(models.Model):
first_name = models.CharField(max_length=20)
last_name = models.CharField(max_length=30)
contact = models.IntegerField()
email = models.EmailField(max_length=50)
age = models.IntegerField() After that apply migration by using the following command.
- python3 manage.py makemigrations myapp
It will create a table myapp_student. The table structure looks like the below.
Leave a Reply