Django provides built-in methods to validate form data automatically. Django forms submit only if it contains CSRF tokens. It uses uses a clean and easy approach to validate data.
The is_valid() method is used to perform validation for each field of the form, it is defined in Django Form class. It returns True if data is valid and place all data into a cleaned_data attribute.
Let’s see an example that takes user input and validate input as well.
Django Validation Example
This example contains the following files and code.
// models.py
from django.db import models
class Employee(models.Model):
eid = models.CharField(max_length=20)
ename = models.CharField(max_length=100)
econtact = models.CharField(max_length=15)
class Meta:
db_table = "employee" Now, create a form which contains the below code.
// forms.py
from django import forms
from myapp.models import Employee
class EmployeeForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Employee
fields = "__all__" Instantiate the form
Instantiate the form, check whether request is post or not. It validate the data by using is_valid() method.
//views.py
def emp(request):
if request.method == "POST":
form = EmployeeForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
try:
return redirect('/')
except:
pass
else:
form = EmployeeForm()
return render(request,'index.html',{'form':form}) Index template that shows form and errors.
// index.html
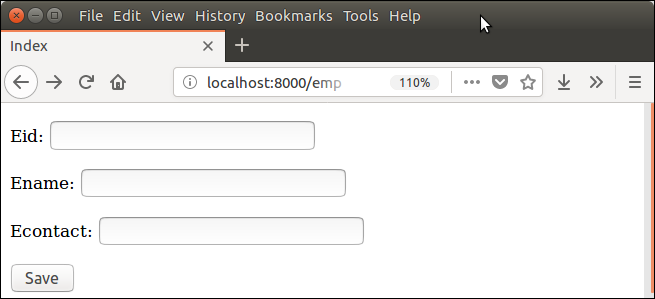
Start server and access the form.
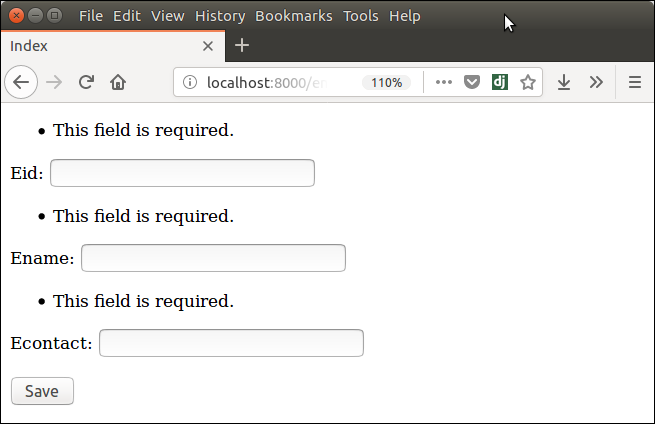
It validates each field and throws errors if any validation fails.
Leave a Reply