HTTP is the hypertext transfer protocol which is considered as the foundation of the data transfer in the world wide web. All web frameworks including flask need to provide several HTTP methods for data communication.
The methods are given in the following table.
| SN | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GET | It is the most common method which can be used to send data in the unencrypted form to the server. |
| 2 | HEAD | It is similar to the GET but used without the response body. |
| 3 | POST | It is used to send the form data to the server. The server does not cache the data transmitted using the post method. |
| 4 | PUT | It is used to replace all the current representation of the target resource with the uploaded content. |
| 5 | DELETE | It is used to delete all the current representation of the target resource specified in the URL. |
We can specify which HTTP method to be used to handle the requests in the route() function of the Flask class. By default, the requests are handled by the GET() method.
POST Method
To handle the POST requests at the server, let us first create a form to get some data at the client side from the user, and we will try to access this data on the server by using the POST request.
login.html
- <html>
- <body>
- <form action = "http://localhost:5000/login" method = "post">
- <table>
- <tr><td>Name</td>
- <td><input type ="text" name ="uname"></td></tr>
- <tr><td>Password</td>
- <td><input type ="password" name ="pass"></td></tr>
- <tr><td><input type = "submit"></td></tr>
- </table>
- </form>
- </body>
- </html>
Now, Enter the following code into the script named post_example.py.
post_example.py
from flask import *
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/login',methods = ['POST'])
def login():
uname=request.form['uname']
passwrd=request.form['pass']
if uname=="ayush" and passwrd=="google":
return "Welcome %s" %uname
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug = True)Now, start the development server by running the script using python post_exmple.py and open login.html on the web browser as shown in the following image.
Give the required input and click Submit, we will get the following result.
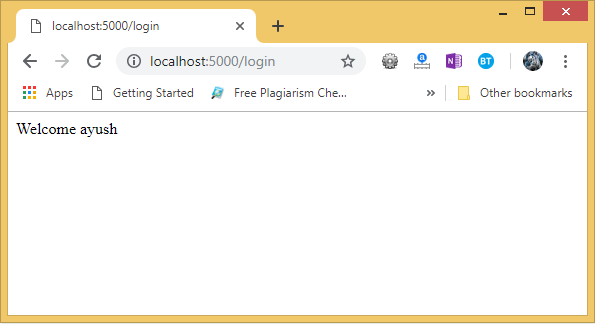
Hence, the form data is sent to the development server by using the post method.
GET Method
Let’s consider the same example for the Get method. However, there are some changes in the data retrieval syntax on the server side. First, create a form as login.html.
login.html
<html>
<body>
<form action = "http://localhost:5000/login" method = "get">
<table>
<tr><td>Name</td>
<td><input type ="text" name ="uname"></td></tr>
<tr><td>Password</td>
<td><input type ="password" name ="pass"></td></tr>
<tr><td><input type = "submit"></td></tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>Now, create the following python script as get_example.py.
get_example.py
- from flask import *
- app = Flask(__name__)
-
-
- @app.route('/login',methods = ['GET'])
- def login():
- uname=request.args.get('uname')
- passwrd=request.args.get('pass')
- if uname=="ayush" and passwrd=="google":
- return "Welcome %s" %uname
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- app.run(debug = True)
Now, open the HTML file, login.html on the web browser and give the required input.
Now, click the submit button.
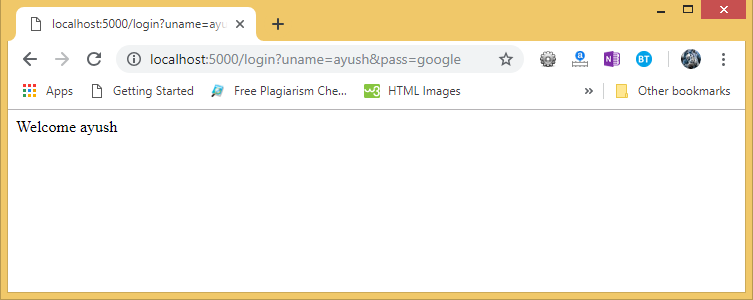
As we can check the result. The data sent using the get() method is retrieved on the development server.
The data is obtained by using the following line of code.
uname = request.args.get('uname') Here, the args is a dictionary object which contains the list of pairs of form parameter and its corresponding value.
In the above image, we can also check the URL which also contains the data sent with the request to the server. This is an important difference between the GET requests and the POST requests as the data sent to the server is not shown in the URL on the browser in the POST requests.
Leave a Reply