Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn about the Python for loop and how to use it to execute a code block a fixed number of times.
Introduction to Python for loop statement with the range() function
In programming, you often want to execute a block of code multiple times. To do so, you use a for loop.
The following illustrates the syntax of a for loop:for index in range(n): statementCode language: Python (python)
In this syntax, the index is called a loop counter. And n is the number of times that the loop will execute the statement.
The name of the loop counter doesn’t have to be index, you can use whatever name you want.
The range() is a built-in function in Python. It’s like the print() function in the sense that it’s always available in the program.
The range(n) generates a sequence of n integers starting at zero. It increases the value by one until it reaches n.
So the range(n) generates a sequence of numbers: 0,1, 2, …n-1. Note that it’s always short of the final number (n).
The following diagram illustrates the for loop statement:
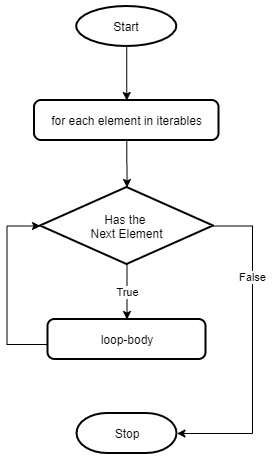
The following example shows how to use the for loop with the range() function to display 5 numbers from 0 to 4 to the screen:
for index in range(5): print(index)Code language: Python (python)Output:
0 1 2 3 4Code language: Python (python)In this example, the for loop executes the statement print(index) exactly five times.
If you want to show 5 numbers from 1 to 5 on the screen, you can do something like this:
for index in range(5): print(index + 1)Code language: Python (python)Output:
1 2 3 4 5Code language: Python (python)In this example, we increase the index by one in each iteration and print it out. However, there’s a better way to do it.
Specifying the starting value for the sequence
By default, the range() function uses zero as the starting number for the sequence.
In addition, the range() function allows you to specify the starting number like this:
range(start, stop)Code language: Python (python)In this syntax, the range() function increases the start value by one until it reaches the stop value.
The following example uses a for loop to show five numbers, from 1 to 5 to the screen:
for index in range(1, 6): print(index)Code language: Python (python)Output:
1 2 3 4 5Code language: Python (python)Specifying the increment for the sequence
By default, the range(start, stop) increases the start value by one in each loop iteration.
To increase the start value by a different number, you use the following form of the range() function:
range(start, stop, step)Code language: Python (python)In this form, you can specify the value that the range() function should increase.
The following example shows all the odd numbers from 0 to 10:
for index in range(0, 11, 2): print(index)Code language: Python (python)Output:
0 2 4 6 8 10Using Python for loop to calculate the sum of a sequence
The following example uses the for loop statement to calculate the sum of numbers from 1 to 100:
sum = 0 for num in range(101): sum += num print(sum)Code language: Python (python)Output:
5050Code language: Python (python)How it works.
- First, the sum is initialized to zero.
- Second, the sum is added with the number from 1 to 100 in each iteration.
- Finally, show the sum to the screen.
By the way, if you’re a mathematician, you can use the simple formula:
n = 100 sum = n * (n+1)/2 print(sum)
Leave a Reply