Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn about the Python while statement and how to use it to run a code block as long as a condition is true.
Introduction to the Python while statement
Python while statement allows you to execute a code block repeatedly as long as a condition is True.
The following shows the syntax of the Python while statement:
while condition: bodyCode language: Python (python)The condition is an expression that evaluates to a boolean value, either True or False.
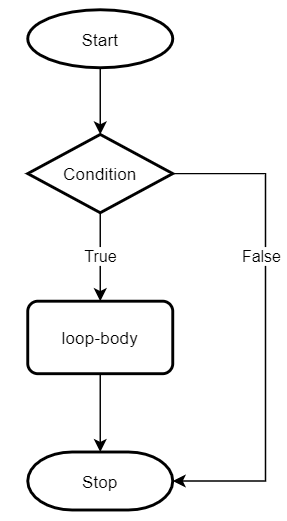
The while statement checks the condition at the beginning of each iteration. It’ll execute the body as long as the condition is True.
In the body of the loop, you need to do something to stop the loop at some time.
Otherwise, you’ll get an indefinite loop that will run forever until you close the application.
Because the while statement checks the condition at the beginning of each iteration, it’s called a pretest loop.
If the condition is False from the beginning, the while statement will do nothing.
The following flowchart illustrates the while loop statement:
Python while statement examples
Let’s take some examples of using the Python while statement.
1) Simple Python while statement example
The following example uses a while statement to show 5 numbers from 0 to 4 to the screen:
max = 5 counter = 0 while counter < max: print(counter) counter += 1Code language: Python (python)Output:
0 1 2 3 4Code language: Python (python)How it works.
- First, define two variables called
maxandcounterwith the initial values of five and zero. - Second, use the
whilestatement with the conditioncounter < max. It’ll execute the loop body as long as the value of thecounteris less than the value ofmax. - Third, show the value of the
countervariable and increase it by one in each iteration. After five iterations, the value of thecounteris 5, which makes the conditioncounter < maxevaluates toFalseand hence the loop stops.
2) Using the Python while statement to build a simple command prompt program
The following example uses the while statement to prompt users for input and echo the command that you entered back. It’ll run as long as you don’t enter the quit command:
command = '' while command.lower() != 'quit': command = input('>') print(f"Echo: {command}") Code language: Python (python)Note that the command.lower() returns the command in lowercase format. This allows you to enter the quit command such as quit, QUIT, or Quit.
Example output:
>Hi Echo: Hi >Python while Echo: Python while >quit Echo: quit
Leave a Reply