Django uses Python’s built-in CSV library to create Dynamic CSV (Comma Separated Values) file. We can use this library in our project’s view file.
Let’s see an example, here we have a Django project to which we are implementing this feature. A view function getfile() is created.
Django CSV Example
In this example, we are creating CSV using static data.
// Views.py
import csv
def getfile(request):
response = HttpResponse(content_type='text/csv')
response['Content-Disposition'] = 'attachment; filename="file.csv"'
writer = csv.writer(response)
writer.writerow(['1001', 'John', 'Domil', 'CA'])
writer.writerow(['1002', 'Amit', 'Mukharji', 'LA', '"Testing"'])
return response// urls.py
Provide url for the function.
path('csv',views.getfile) While executing to the browser, it renders a CSV file. See the example.
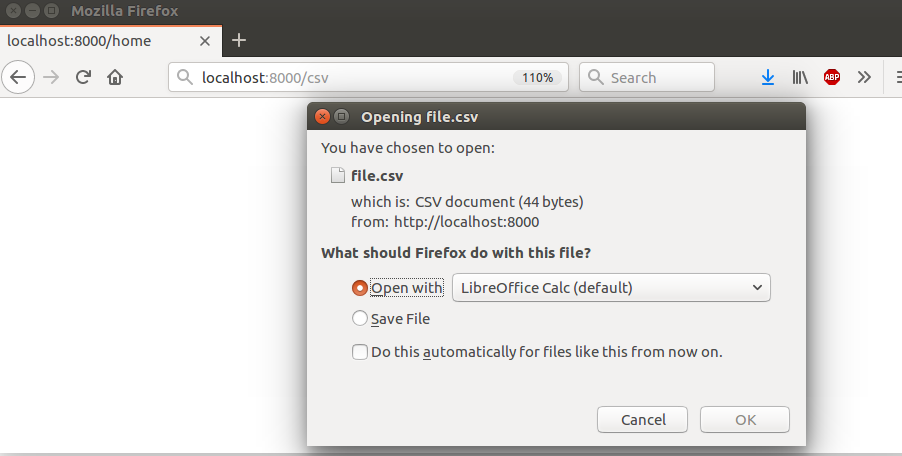
Apart from static data, we can get CSV from the database too. See, the following example in which we are getting data from the table by using the Employee model.
Dynamic CSV using Database
// views.py
from myapp.models import Employee import csv
def getfile(request):
response = HttpResponse(content_type='text/csv')
response['Content-Disposition'] = 'attachment; filename="file.csv"'
employees = Employee.objects.all()
writer = csv.writer(response)
for employee in employees:
writer.writerow([employee.eid,employee.ename,employee.econtact])
return responseOutput:
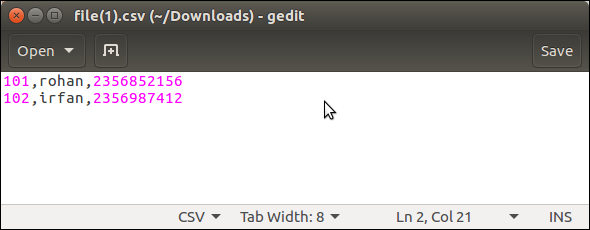
Save the file and open into the text editor that contains the following data.
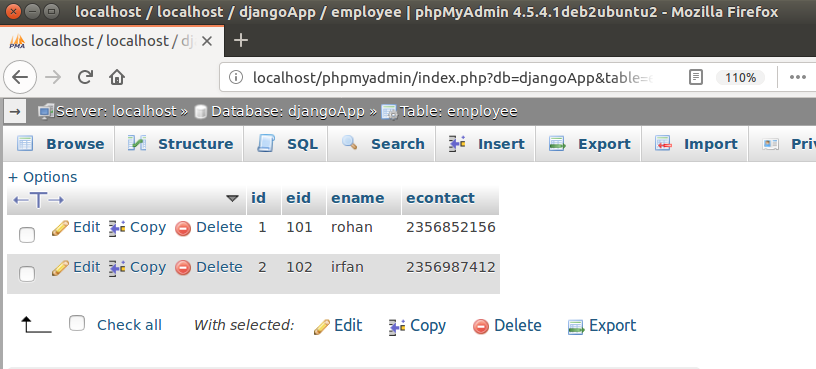
This data is retrieved from the table employee, a snapshot of the table is shown below.
Leave a Reply